What Is HDR? What Does HDR Stand For?

What Is HDR? What Does HDR Stand For?
As the display technologies on the market become more mature, the development of technology has given us different choices for displays. As a widely concerned display technology, HDR is currently widely used. When choosing a monitor, we need to understand the relevant basic knowledge in order to better choose the display screen.
What is HDR?
What does hdr meaning? HDR is a processing technology that improves the brightness and contrast of images. This technology can enrich the details of each dark part, make dark places darker, and enrich more detailed colors, so that movies, pictures, and game screens can all present excellent images. The effect makes users closer to the visual experience in the real environment when watching movies and playing games. The maximum brightness of traditional SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) is only 100 nits, the part of the picture higher than 100 nits will be distorted (lost), the minimum adjustment is 0.1 nits, and the part of the picture lower than 0.1 nits will be lost. HDR technology can make the highest brightness reach thousands of nits and the lowest brightness reach 0.0005 nits, which greatly expands the details of the parts with brightness higher than 100 nits and lower than 0.1 nits in the picture, and makes the whole picture look more transparent Bright and detailed.Just like our 4k hdr monitor provides you with a high quality and vivid image.
HDR stands for High Dynamic Range and can display a wider range of brightness (dynamic range) -- from the darkest to the brightest -- than the existing SDR (Standard Dynamic Range).
As shown in the image below, when displaying content in SDR, blacks in shadows appear to be crushed, while whites in bright areas have a washed-out appearance; while HDR allows for a more natural, true-to-life display without diluting brights or darks The hue of the region.
HDR is attracting attention as the next generation of high-quality imaging technology, and content produced in the HDR format is now available through video streaming services such as Netflix and UHD Blu-ray Disc.

SDR- crushed black in shadow

SDR- white in bright areas is washed out

HDR
What does hdr mean? HDR principle
The brightness of our screen cannot reach the brightness that can perfectly restore the color information in the material, and the processing of the brightness information in the HDR video that exceeds its brightness display range will produce an overexposed or too dark picture. For TVs, the solution is to greatly increase the brightness of the screen. Currently, HDR TVs require a maximum brightness of at least 1000 nits and a minimum brightness of at least 0.05 nits.
However, the usage distance limit of computer monitors directly limits the brightness range of the monitor (the brightness of the monitor exceeding 500 nits will cause damage to human eyes), so the way to achieve HDR for computer monitors is not the same as that of TVs. The HDR support chip in the HDR display is deployed according to the display parameters. It will analyze the HDR content, extract the brightness information, and perform tone mapping on the information in the HDR content that exceeds the dynamic range and color of the display (for a large contrast attenuation. Change the brightness of the scene to the range that can be displayed, while maintaining image details and colors that are very important to express the original scene), the monitor screen will emphasize every exposure detail of the HDR film source in the displayed picture.
According to this principle, the details of the highlights in the film source can be displayed more clearly, improving the picture quality and displaying more realistically.Getting hdr monitors will definitely enhance the experience whether watching movies or playing games.

Five Elements of High Image Quality
These five elements affect the quality of the image
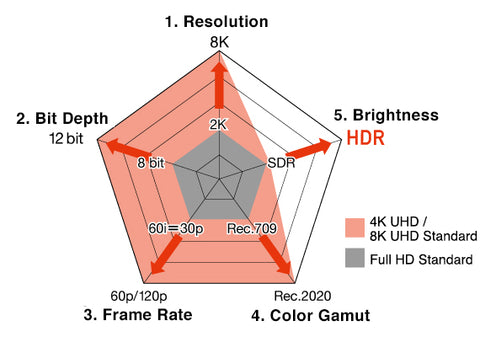
Among them, the resolution, bit depth, frame rate, and color gamut have been standardized according to the 4K/8K UHD broadcast standard BT.2020. *Only the brightness standard still stays at 100 cd/m² stipulated in the full HD broadcasting standard BT.709, without any improvement.
Because of this, production efforts to date have required compressing high-brightness portions of images to match the characteristics of display devices, resulting in displayed images that differ from the original scene.
In recent years, however, advances in display technology have resulted in an increase in the dynamic range that can be displayed, allowing brightness and color reproduction to truly resemble those seen in the real world.This is why HDR has been getting so much attention lately.
1.Resolution = fineness of image detail
Resolution refers to the number of pixels in an image. The higher the resolution, the more pixels there are for a given screen size, resulting in finer details. 4K UHD resolution is 3840x2160, which means four times the image data displayed is standard Full HD.

2K

4K

8K
2.Bit depth = how fine the color gradient is
Bit depth refers to the number of colors each pixel can display. The greater the bit depth, the more colors can be displayed, resulting in smoother, more natural gradients. For example, an 8-bit monitor can display about 16.77 million colors, while a 10-bit monitor can display about 1.07 billion colors.

8-digit display

10-digit display
3.Frame rate = smoothness of motion
Frame rate refers to the number of images displayed in one second. Movies typically have a frame rate of 24p (24 pictures, or frames per second), while standard television typically has a frame rate of 60i or 30p (30 frames per second).
The 8K broadcast standard BT.2020 includes the definition of frame rates (up to 120p) at which motion is nearly as smooth as in the real world.

30p = 60i

60p

120p
4.Color gamut = how vivid the colors are
Color gamut refers to the range of all colors that can be displayed. The chart on the right shows the range of all RGB values that the human eye can perceive. The triangles represent the color gamut: the larger the triangle, the more colors that can be displayed.
The 4K/8K broadcast standard BT.2020 (Rec.2020) covers a wider range of colors than the existing full HD broadcast standard BT.709 (Rec.709).

5.Brightness = intensity of image lighting
Brightness refers to the range of image lighting intensity that can be displayed. The range of difference between the darkest and brightest objects that the human eye can perceive (dynamic range) is usually 1012, while traditional display devices can only display a dynamic range of up to 103. HDR extends the dynamic range to 105 - 100 times higher than current display devices - allowing light and shadow to be presented in a way that is closer to what the human eye perceives.

What are the standards for HDR?
There are six different standards in common: hdr10, Dolby Vision, hdr10+, HLG, Advanced HDR by Technicolor, and DisplayHDR.
What is HDR10?
HDR10 turns out to be the most common HDR out there. It's an open standard that has been adopted by numerous service providers, such as Amazon and Netflix. According to CEA (Consumer Electronics Association), hdr10 must meet certain standards, including 4:2:0 color sampling, 10bit color depth and bt.2020 color space, which is the general rule of HDR and the most basic HDR standard.
HDR10 is the standard pushed by the UHD Alliance. It's a technical standard with defined ranges and specifications that must be met for content and displays to qualify as using it. HDR10 uses static metadata that is consistent across all displays. This means HDR10 video sets light and color levels in absolute values, regardless of the screen it's being shown on. It's an open standard, so any content producer or distributor can use it freely. Every service with HDR content supports HDR10, usually along with Dolby Vision or another HDR format.
What is HDR10+?
Samsung's HDR standard. Just like Dolby vision HDR, Samsung's HDR technology uses dynamic metadata in compatible content to upscale the HDR image frame by frame. It builds on HDR10 by adding dynamic metadata, like Dolby Vision. It doesn't use individualized metadata for each screen, but it still adjusts the range of light it tells the TV to display for each scene or frame. It can potentially add more detail to your picture over what HDR10 shows, and like HDR10 it's an open standard that doesn't require licensing with a very specific production workflow. Amazon Prime Video is the first content provider to announce hdr10+ support, and live broadcast in HDR10+ mode to provide more than 100 shows, such as <The Man In The High Castle> and <Grand Tour>.
What is Dolby Vision?
The key difference between Dolby Vision and HDR10 is that while HDR10 applies its parameters from scene to scene, Dolby Vision allows dynamic metadata to complement and adapt the HDR image frame by frame. In theory, Dolby Vision can process images more subtly and improve picture quality, but in reality, picture quality depends on how well the film can use this technology. Currently, a small number of Sony films use Dolby Vision.
One of the things that makes Dolby Vision different is that it's designed as an end-to-end HDR process. So from capture through processing and into production, Dolby Vision is designed to preserve information that was originally captured and pass it on. It does this using metadata that's then read by the Dolby Vision decoder on the TV you're watching. The aim is to give you an HDR experience that's closer to the original by supplying more information - and it does this by using dynamic metadata.
What is HLG?
Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG) isn't as common as HDR10 or Dolby Vision, and there's very little content for it yet outside of some BBC and DirecTV broadcasts, but it could make HDR much more widely available. That's because it was developed by the BBC and Japan's NHK to provide a video format that broadcasters could use to send HDR signals (and SDR; HLG is backward-compatible). It's technically more universal because it doesn't use metadata at all; instead, it uses a combination of the gamma curve that TVs use to calculate brightness for SDR content and a logarithmic curve to calculate the much higher levels of brightness that HDR-capable TVs can produce (hence the name Hybrid Log-Gamma).
What is Advanced HDR by Technicolor?
Advanced HDR by Technicolor is a newer HDR format that was introduced at CES (International Consumer Electronics Show) in 2017. It's the result of a collaboration between LG and video specialist Technicolor, but LG is the only one currently supporting the format. However, the official did not release any specific news and supported content of its HDR.
What is DisplayHDR?
This is the HDR standard set by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) for PC monitors. DisplayHDR version 1.0 is divided into three levels, DisplayHDR 400, DisplayHDR 600, and DisplayHDR, according to characteristics such as lumens, color gamut, color depth, and rise time. 1000. At present, the DisplayHDR certification specification is only for LCD displays for the time being, and does not apply to OLED panels, nor is it guaranteed to be compatible with existing HDR content and games. This standard was just released at the end of 2017. It is expected that more display manufacturers will adopt this standard in the future, but this standard only targets the hardware capabilities of the display.














Leave a comment